Introduction
In the realm of artificial intelligence (AI), the latest breakthrough known as Generative AI has been making waves across various industries, promising transformative outcomes for enterprises. This article delves into the significance of Generative AI for enterprises, exploring its capabilities, applications, and potential impact on business operations.
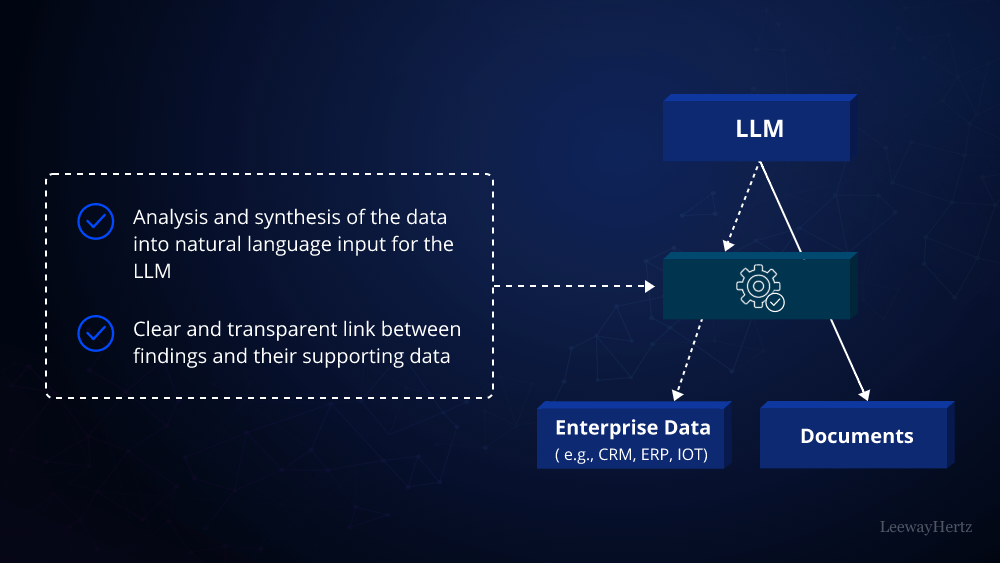
Understanding Generative AI
Generative AI refers to a class of algorithms that can generate new data or content, often mimicking human-like creativity and intuition. Unlike traditional AI models that focus on classification or prediction tasks, Generative AI enables machines to produce original outputs, such as images, text, music, and even entire narratives. This revolutionary technology has the potential to revolutionize how enterprises approach tasks ranging from content creation to product design and beyond.
Applications in Enterprises
Generative AI holds immense promise for enterprises across various sectors, offering innovative solutions to longstanding challenges. Here are some key applications:
- Content Creation: Enterprises can leverage Generative AI to automate content creation processes, including generating articles, product descriptions, marketing materials, and social media posts. By harnessing AI-powered tools, businesses can enhance efficiency, scale content production, and maintain consistency across different channels.
- Design and Creativity: From graphic design to architectural planning, Generative AI empowers enterprises to explore new frontiers of creativity. By generating design prototypes, artwork, and architectural blueprints, businesses can streamline the creative process, iterate rapidly, and uncover novel solutions to design challenges.
- Personalized Customer Experiences: Generative AI enables enterprises to deliver highly personalized customer experiences across digital platforms. By analyzing vast datasets and synthesizing customer preferences, businesses can generate tailored recommendations, product suggestions, and interactive experiences that resonate with individual users.
- Virtual Assistants and Chatbots: Enterprises can enhance customer service and streamline internal operations by deploying Generative AI-powered virtual assistants and chatbots. These intelligent agents can engage in natural language conversations, answer inquiries, provide support, and automate routine tasks, thereby improving efficiency and enhancing user satisfaction.
- Data Augmentation and Synthesis: Generative AI algorithms can generate synthetic data to augment training datasets for machine learning models. By generating diverse and representative data samples, enterprises can improve the performance and robustness of AI systems, particularly in scenarios where real-world data is scarce or costly to obtain.
Challenges and Considerations
While Generative AI holds tremendous potential, its adoption in enterprises is not without challenges and considerations. Here are some key factors to keep in mind:
- Ethical and Legal Implications: The use of Generative AI raises ethical concerns related to data privacy, intellectual property rights, and the potential misuse of AI-generated content. Enterprises must navigate complex regulatory landscapes and establish clear guidelines for responsible AI usage to mitigate risks and uphold ethical standards.
- Quality and Reliability: Generating high-quality outputs with Generative AI requires careful fine-tuning of algorithms and validation processes. Enterprises must invest in robust quality assurance mechanisms to ensure that AI-generated content meets desired standards of accuracy, relevance, and coherence.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Integrating Generative AI solutions into existing enterprise systems and workflows may pose technical challenges, requiring compatibility with legacy infrastructure, data formats, and software platforms. Enterprises should conduct thorough assessments of integration requirements and develop tailored implementation strategies to minimize disruptions and maximize synergies.
- Human-AI Collaboration: While Generative AI can automate repetitive tasks and augment human capabilities, it is not a substitute for human creativity, intuition, and domain expertise. Enterprises should foster a culture of collaboration between humans and AI systems, enabling employees to leverage AI tools as enablers rather than replacements for human ingenuity.
- Continuous Learning and Adaptation: Generative AI models require ongoing training and refinement to adapt to evolving business needs, user preferences, and market dynamics. Enterprises should allocate resources for continuous learning and experimentation, fostering a culture of innovation and agility to harness the full potential of Generative AI over time.
Conclusion
Generative AI represents a paradigm shift in how enterprises harness the power of artificial intelligence to drive innovation, creativity, and efficiency. By leveraging Generative AI technologies, businesses can unlock new opportunities for content creation, design, personalization, automation, and data synthesis, paving the way for transformative outcomes in the digital era. However, successful adoption of Generative AI requires careful consideration of ethical, technical, and organizational factors, as well as a commitment to continuous learning and collaboration between humans and machines. As enterprises embark on their Generative AI journey, they must navigate challenges with foresight and diligence, ensuring that AI-powered innovation is harnessed responsibly for the benefit of society and the future of work.
Leave a comment