Introduction
In the rapidly evolving world of artificial intelligence, the term “Generative AI tech stack” has become a significant point of interest. This stack is fundamental in developing advanced AI systems capable of creating new, innovative content, from text and images to music and beyond. In this article, we will break down the Generative AI tech stack, focusing on its core components, functionalities, and the impact it has on various industries. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast or a professional looking to implement Generative AI, this guide will provide clear insights into how the Generative AI tech stack works and its potential.
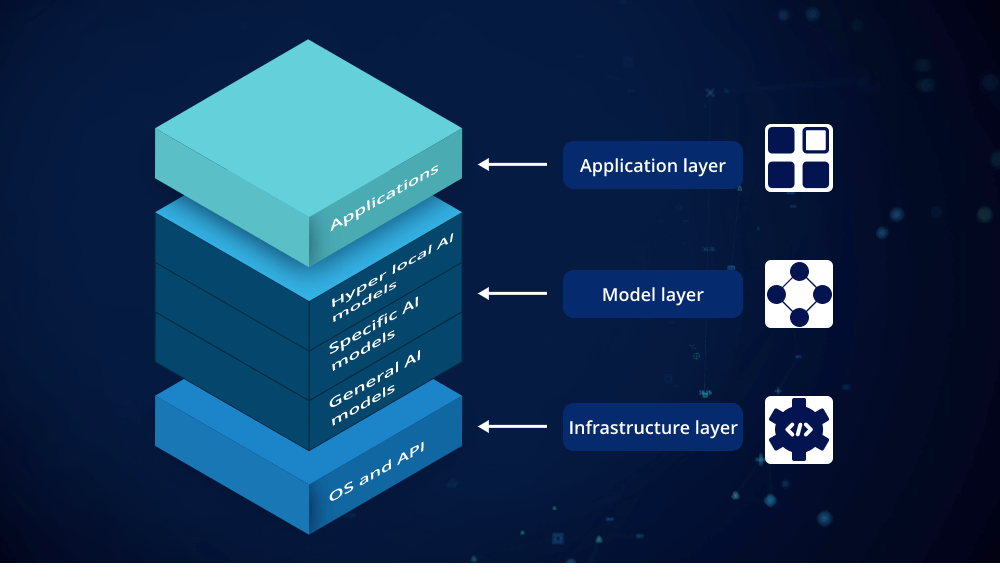
What is the Generative AI Tech Stack?
The Generative AI tech stack refers to the collection of technologies and frameworks that work together to create generative AI models. These models are designed to generate new data or content that resembles real-world data, using sophisticated algorithms and machine learning techniques. The tech stack typically includes several layers, each playing a crucial role in the overall functionality of generative AI systems.
1. Data Collection and Preparation
The foundation of any Generative AI tech stack is data. High-quality data collection and preparation are critical to training effective generative models. This involves gathering large datasets relevant to the task, cleaning the data, and preprocessing it to ensure it is suitable for training. In this phase, data augmentation techniques may also be employed to increase the diversity and quantity of data available, improving the model’s performance and generalization capabilities.
2. Model Architecture
At the heart of the Generative AI tech stack is the model architecture. This refers to the specific structure and design of the AI models used to generate new content. Some popular generative models include:
- Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): Consist of two neural networks, the generator and the discriminator, that compete against each other to produce high-quality synthetic data.
- Variational Autoencoders (VAEs): Use probabilistic techniques to encode input data into a latent space and then decode it back to generate new samples.
- Transformers: Known for their success in natural language processing, transformers can also be adapted for generative tasks, such as generating text or other sequential data.
Each model architecture has its strengths and is chosen based on the specific requirements of the task.
3. Training and Optimization
Once the model architecture is defined, the next step in the Generative AI tech stack is training and optimization. This involves feeding the prepared data into the model and adjusting the model’s parameters to minimize errors and improve accuracy. Training generative models often requires significant computational resources and time. Techniques such as hyperparameter tuning, regularization, and optimization algorithms (like Adam or SGD) are used to enhance the model’s performance and efficiency.
4. Evaluation and Validation
After training, the generative model must be evaluated and validated to ensure it meets the desired standards. This involves assessing the quality and relevance of the generated content. Metrics such as Inception Score (IS) or Fréchet Inception Distance (FID) are commonly used to quantify the performance of generative models. Additionally, human evaluation might be employed to provide qualitative feedback on the model’s output.
5. Deployment and Integration
Once validated, the generative model is ready for deployment. This stage involves integrating the model into production environments where it can generate content in real-world applications. The Generative AI tech stack must include robust infrastructure for deploying models, such as cloud services or on-premises solutions. Additionally, APIs and user interfaces are developed to facilitate interaction with the model and ensure it can be easily utilized by end-users.
6. Continuous Improvement
The Generative AI tech stack is not static; it requires ongoing maintenance and improvement. Continuous learning and adaptation are crucial to keep the model updated with new data and to enhance its capabilities over time. This phase may involve retraining the model with fresh data, fine-tuning it based on user feedback, and incorporating advancements in AI research.
Applications of Generative AI
The Generative AI tech stack has a wide range of applications across various industries. In content creation, generative models can produce realistic images, videos, and music. In the field of healthcare, they can assist in generating synthetic medical data for research purposes. In the entertainment industry, generative AI can create engaging and interactive experiences, such as personalized video game content or automated storytelling.
Conclusion
The Generative AI tech stack represents a powerful combination of technologies and methodologies that enable the creation of innovative and diverse content. By understanding the core components—data collection, model architecture, training, evaluation, deployment, and continuous improvement—individuals and organizations can harness the potential of generative AI to drive progress and creativity. As the field of generative AI continues to advance, staying informed about the latest developments in the Generative AI tech stack will be essential for leveraging its full capabilities.
Leave a comment