In the world of artificial intelligence and machine learning, Multimodal Models are gaining significant attention. These models integrate and analyze multiple types of data—such as text, images, and audio—to improve the accuracy and depth of machine learning applications. This article will delve into what Multimodal Models are, how they work, their applications, and their impact on technology.
What Are Multimodal Models?
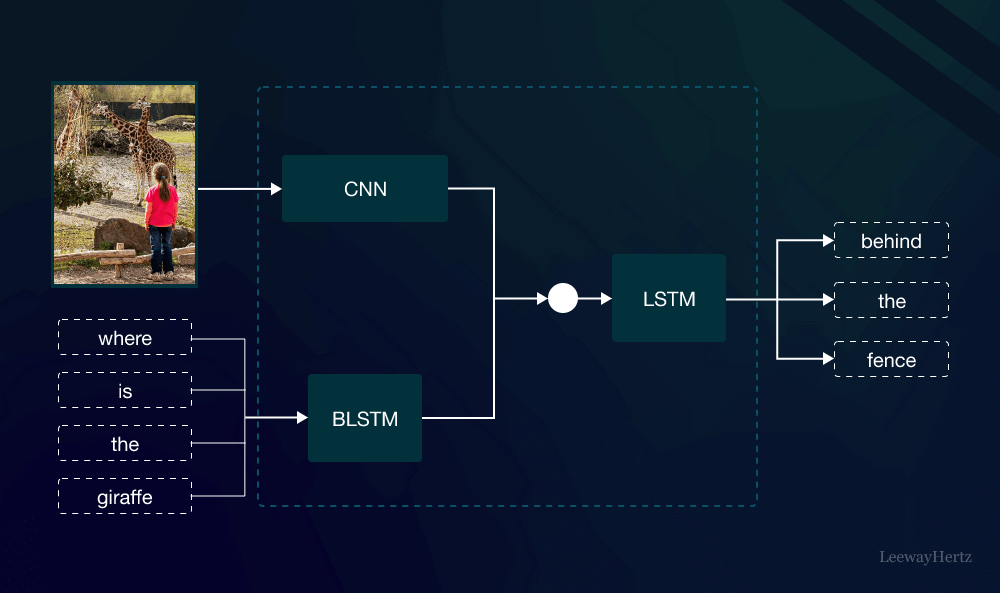
Multimodal Models refer to machine learning systems designed to process and understand different kinds of data inputs simultaneously. Unlike traditional models that may specialize in a single type of data, such as text-only or image-only data, Multimodal Models combine various modalities. These can include text, images, audio, and more, allowing the model to gain a richer and more comprehensive understanding of the information.
For example, a Multimodal Model could analyze a video by processing both the visual elements (images) and the spoken dialogue (audio) to provide more nuanced insights compared to a model focusing on just one type of data.
How Do Multimodal Models Work?
Multimodal Models work by integrating different types of data inputs into a unified framework. The process generally involves several steps:
- Data Processing: Different types of data are first processed separately. For instance, text might be tokenized and embedded into vectors, while images might be transformed into feature maps using convolutional neural networks.
- Fusion: The processed data from various modalities are combined into a single representation. This fusion can occur at different stages of the model’s architecture, depending on the complexity and design of the model.
- Analysis: The unified data representation is then analyzed using machine learning algorithms. This stage enables the model to draw insights from the combined data, improving the model’s ability to understand and generate responses or predictions.
- Output Generation: Finally, the model produces an output based on the combined insights from the multimodal data. This output could be anything from a text description of an image to a detailed response based on both visual and auditory information.
Applications of Multimodal Models
Multimodal Models have a wide range of applications across various fields. Here are some key areas where these models are making a significant impact:
- Healthcare: In medical diagnostics, Multimodal Models can analyze patient data from multiple sources, such as medical images, electronic health records, and patient interviews. This integrated approach can lead to more accurate diagnoses and personalized treatment plans.
- Autonomous Vehicles: For self-driving cars, Multimodal Models process data from cameras, radar, and LiDAR sensors. By combining these data sources, the model can better understand the vehicle’s surroundings, enhancing safety and navigation.
- Content Creation: In multimedia content creation, these models can generate descriptive text for images or videos, and even create content that seamlessly integrates text and visuals, providing richer and more engaging user experiences.
- Assistive Technologies: Multimodal Models are also used in assistive technologies for individuals with disabilities. For instance, combining speech recognition and image recognition can help in developing tools that assist visually impaired users by providing detailed descriptions of their environment.
Challenges and Future Directions
While Multimodal Models offer promising advancements, they also face several challenges:
- Data Integration: Combining different types of data effectively remains a complex task. Ensuring that the data from various modalities are aligned and contribute equally to the model’s understanding is crucial.
- Computational Complexity: Processing and integrating multiple data types can be computationally intensive. This requires significant resources and optimization to ensure efficiency.
- Data Quality: The performance of Multimodal Models heavily relies on the quality of the data. Inaccurate or biased data can lead to misleading outcomes and reduce the effectiveness of the model.
Looking ahead, the development of Multimodal Models is likely to focus on improving data integration techniques, reducing computational demands, and enhancing the robustness of models against noisy or incomplete data. Advances in hardware and algorithms will further propel the capabilities of these models, leading to even more innovative applications.
Conclusion
Multimodal Models represent a significant leap forward in the field of artificial intelligence by integrating various types of data to provide more comprehensive and accurate insights. Their ability to combine text, images, audio, and other data forms allows for a deeper understanding of complex information, making them invaluable in numerous applications from healthcare to autonomous vehicles.
As technology continues to evolve, the potential for Multimodal Models is vast, promising even greater advancements and opportunities in the future. Understanding and leveraging these models will be key for developers and researchers looking to harness the full potential of machine learning in the coming years.
Leave a comment