Generative AI has become a cornerstone of modern technology, enabling applications that range from creating art to generating human-like text. However, to leverage the full potential of Generative AI, it is crucial to understand how to fine-tune a pre-trained model for these applications. This article will guide you through the process, ensuring your AI models are optimized for your specific use cases.
Understanding the Importance of Fine-Tuning a Pre-Trained Model
Before diving into the steps, it’s essential to understand why fine-tuning a pre-trained model is necessary for Generative AI applications. Pre-trained models are built on massive datasets and are designed to perform a wide range of tasks. However, they might not be perfectly suited for specific applications without additional training. Fine-tuning allows you to adapt these models to your unique requirements, enhancing their performance and accuracy.
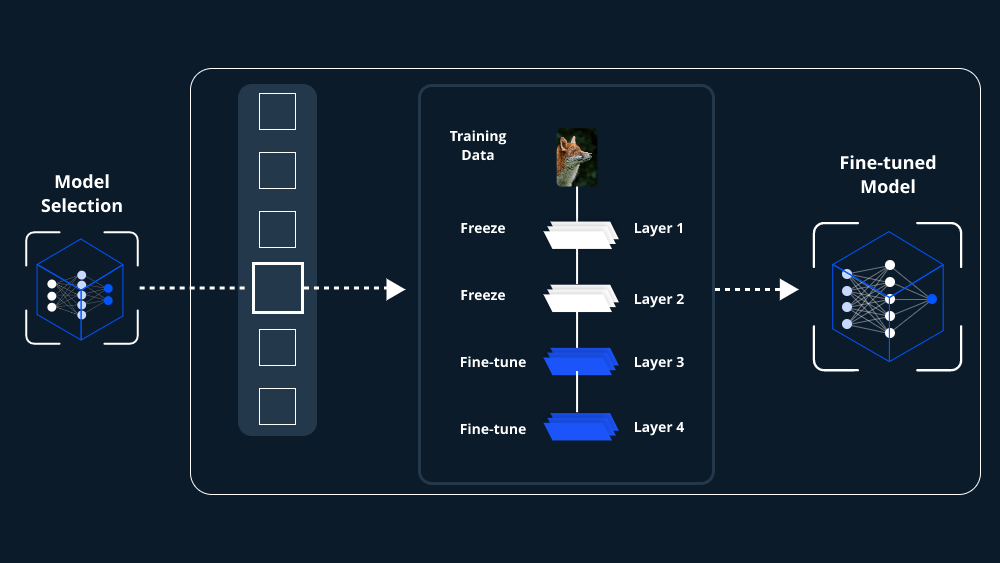
Step 1: Selecting the Right Pre-Trained Model
The first step in fine-tuning a pre-trained model for Generative AI applications is selecting the appropriate base model. Numerous models are available, each designed for different tasks such as image generation, text generation, or even music composition.
- Choosing the Model Based on Your Task: For text generation, models like GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) are widely used. For image-related tasks, models like StyleGAN or DALL·E might be more suitable.
- Considering Model Size and Resources: Larger models typically offer better performance but require more computational resources. Assess your hardware capabilities before choosing a model.
Step 2: Preparing Your Dataset
Once you’ve selected a pre-trained model, the next step is to prepare your dataset. The quality and relevance of your dataset are crucial when you fine-tune a pre-trained model for Generative AI applications.
- Dataset Relevance: Ensure your dataset is closely related to your intended application. For example, if you’re working on text generation in the medical field, your dataset should consist of medical literature.
- Data Preprocessing: Clean your dataset by removing noise, normalizing data, and ensuring it’s in the correct format. This step may include tokenization for text data or resizing images for image generation tasks.
Step 3: Fine-Tuning the Model
With your dataset ready, you can begin to fine-tune the pre-trained model. This step is where the model learns to adapt to your specific data.
- Adjusting the Learning Rate: Fine-tuning typically requires a lower learning rate than training from scratch. Start with a small learning rate to avoid overshooting the optimal solution.
- Freezing Layers: Depending on your application, you might not need to train all layers of the model. Freezing some layers can help retain the knowledge the model has already learned while focusing on the most relevant parts.
- Training the Model: Train your model on your dataset. Monitor the training process closely to avoid overfitting, where the model performs well on the training data but poorly on unseen data.
Step 4: Evaluating the Model
After fine-tuning, it’s crucial to evaluate the model to ensure it performs well in Generative AI applications.
- Using Validation Data: Separate a portion of your dataset for validation. This data should not have been used during the training phase, ensuring an unbiased evaluation of the model’s performance.
- Performance Metrics: Depending on your application, choose appropriate metrics to evaluate your model. For text generation, you might look at perplexity, while for image generation, Inception Score (IS) or Fréchet Inception Distance (FID) might be more relevant.
Step 5: Optimizing the Fine-Tuned Model
Even after fine-tuning, there’s often room for improvement. Optimization techniques can help you get the best performance from your fine-tuned model for Generative AI applications.
- Hyperparameter Tuning: Experiment with different hyperparameters like learning rate, batch size, and number of epochs. Fine-tuning these can significantly impact model performance.
- Data Augmentation: In cases where you have limited data, augmenting your dataset with slight variations can help improve model robustness.
- Regularization Techniques: Applying techniques such as dropout can prevent overfitting and improve the model’s ability to generalize to new data.
Step 6: Deploying the Fine-Tuned Model
Once you’re satisfied with your fine-tuned model’s performance, it’s time to deploy it in your Generative AI application.
- Exporting the Model: Convert the model to a format compatible with your deployment environment. For example, TensorFlow models might be saved in a .pb format, while PyTorch models could be saved as .pt files.
- Integrating with Applications: Embed the model into your application. Whether it’s a web service, mobile app, or desktop application, ensure the model runs efficiently in your chosen environment.
- Monitoring and Updating: Post-deployment, continually monitor the model’s performance. Generative AI applications might require regular updates to the model as new data becomes available or as the application evolves.
Conclusion
Fine-tuning a pre-trained model for Generative AI applications is a multi-step process that requires careful consideration at each stage. From selecting the right model and preparing your dataset to optimizing and deploying the model, every step plays a critical role in the success of your AI application. By following this guide, you can enhance the performance of your Generative AI models, ensuring they meet the specific needs of your application and deliver the desired results.
By understanding and applying these techniques, you will be well-equipped to fine-tune a pre-trained model for Generative AI applications, ultimately creating more sophisticated, reliable, and powerful AI-driven solutions.
Leave a comment