Multi-agent systems (MAS) are a fascinating and rapidly evolving field within artificial intelligence and computer science. These systems consist of multiple agents that interact with one another to achieve individual and collective goals. This article delves into the types of multi-agent systems, their working mechanisms, applications, and benefits.
Types of Multi-Agent Systems
Multi-agent systems can be classified into several types based on their structure and functionality. The main types include:
- Collaborative Multi-Agent Systems: In these systems, agents work together to achieve a common goal. They share information and resources to solve complex problems that would be difficult for a single agent. Examples include distributed robotics and collaborative filtering systems.
- Competitive Multi-Agent Systems: Here, agents operate in environments where they compete against each other for resources or objectives. This type often applies to scenarios like auctions or game theory applications where agents have conflicting interests.
- Hybrid Multi-Agent Systems: Combining elements of both collaborative and competitive systems, hybrid MAS can switch between cooperative and competitive modes depending on the context. They are versatile and can handle a variety of scenarios, making them suitable for complex and dynamic environments.
- Adaptive Multi-Agent Systems: These systems have agents that can learn and adapt over time. They are designed to improve their performance based on experiences and changing environments. Examples include systems for dynamic scheduling and adaptive network management.
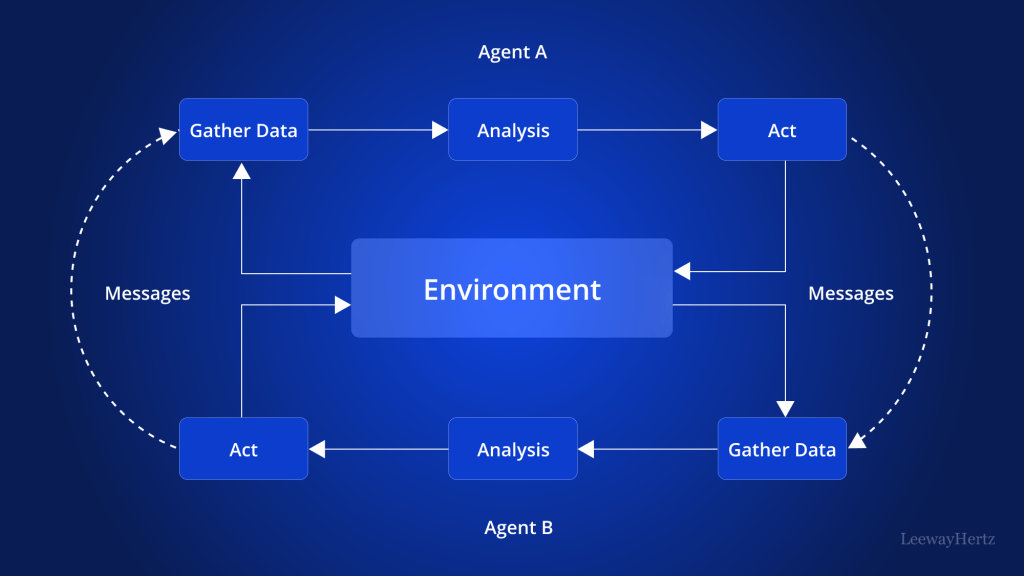
Working of Multi-Agent Systems
The functionality of multi-agent systems revolves around the interactions among agents and their environment. Here’s a simplified explanation of how MAS work:
- Agents: In a MAS, agents are autonomous entities that perceive their environment through sensors and act upon it through actuators. Each agent has its own goals, capabilities, and knowledge base.
- Interaction: Agents interact with each other through communication. They exchange information, negotiate, and collaborate to achieve their objectives. Communication can be direct (like sending messages) or indirect (like leaving signals in the environment).
- Coordination: Coordination mechanisms are essential for ensuring that agents work together efficiently. This can involve negotiation, cooperation, or even conflict resolution. Coordination helps align the agents’ actions toward a common goal or balance their competitive interests.
- Adaptation: Many MAS are designed to adapt to changing environments or learn from interactions. Adaptive mechanisms allow agents to modify their behavior based on new information or experiences, enhancing their ability to handle dynamic conditions.
Applications of Multi-Agent Systems
Multi-agent systems have a wide range of applications across various fields. Here are some notable examples:
- Robotics: In robotics, MAS are used for tasks like swarm robotics, where multiple robots work together to complete tasks such as search and rescue missions, environmental monitoring, or assembly line operations.
- Transportation: MAS are applied in traffic management systems to optimize the flow of vehicles, reduce congestion, and improve safety. Intelligent transportation systems use MAS to coordinate traffic lights and manage public transportation effectively.
- Healthcare: In healthcare, MAS can manage patient care by coordinating between different medical professionals and resources. They also support telemedicine systems, where agents handle patient data, schedules, and communications.
- Finance: Financial markets utilize MAS for algorithmic trading, where agents make buy and sell decisions based on market data and trends. MAS help in predicting market movements and managing risks efficiently.
- Smart Cities: MAS contribute to the development of smart cities by managing resources like energy, water, and waste. They enable the integration of various city services, enhancing the overall quality of life for residents.
Benefits of Multi-Agent Systems
The use of multi-agent systems offers several significant benefits:
- Scalability: MAS can easily scale to handle larger and more complex tasks. By adding more agents, the system can manage more resources or address more extensive problems without a major overhaul.
- Flexibility: The adaptive nature of MAS allows them to function in dynamic and unpredictable environments. They can adjust their behavior based on changing conditions, making them suitable for real-world applications.
- Robustness: Multi-agent systems are generally more robust and resilient to failures. If one agent fails, others can continue to operate, ensuring the system’s overall stability and reliability.
- Efficiency: MAS can optimize performance by distributing tasks among agents, reducing bottlenecks, and improving the speed and accuracy of problem-solving. This distributed approach often leads to more efficient resource utilization.
- Improved Decision-Making: By leveraging collective intelligence and collaboration, MAS can make better decisions than individual agents working alone. This is particularly useful in complex decision-making scenarios where diverse inputs are valuable.
In summary, multi-agent systems represent a powerful approach to solving complex problems through the interaction and coordination of multiple autonomous agents. By understanding the types, working mechanisms, applications, and benefits of MAS, one can appreciate the significant impact they have across various industries. Their ability to adapt, scale, and collaborate makes them a critical component of modern technological advancements.
Leave a comment