Introduction
In recent years, machine learning has made significant strides, especially in natural language processing, computer vision, and other AI applications. One of the critical challenges, however, is the high computational cost and extensive memory requirements associated with training large models. Parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) has emerged as a promising approach to address these issues, enabling the fine-tuning of pre-trained models without the need to adjust all their parameters. This article explores the basics, benefits, and applications of PEFT, providing a comprehensive overview of this innovative technique.
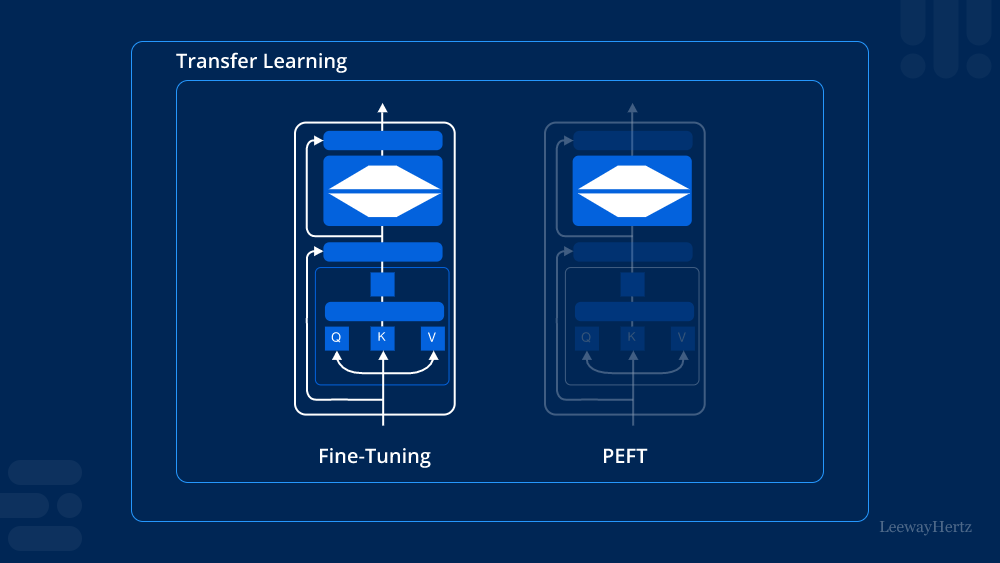
What is Parameter-efficient Fine-tuning (PEFT)?
Parameter efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) is a method that allows machine learning models to be fine-tuned with minimal parameter updates. Unlike traditional fine-tuning, which requires adjusting a vast number of parameters in a model, PEFT focuses on modifying a smaller subset of parameters. This approach significantly reduces computational costs and memory usage, making it ideal for applications where resources are limited or where rapid deployment is needed.
How Does Parameter-efficient Fine-tuning Work?
PEFT operates on the principle that not all parameters of a pre-trained model need to be updated for it to adapt to new tasks. By identifying and fine-tuning only the most critical parameters, PEFT maintains the model’s overall performance while minimizing the changes needed. Techniques like adapter layers, low-rank adaptation, and parameter freezing are commonly used in PEFT. These methods selectively adjust parts of the model, such as intermediate layers or specific components, to achieve the desired performance with fewer resources.
Benefits of Parameter-efficient Fine-tuning (PEFT)
- Reduced Computational Costs: One of the primary advantages of PEFT is its ability to cut down on computational requirements. By updating only a fraction of the model’s parameters, PEFT reduces the amount of processing power needed, which in turn lowers operational costs and accelerates the fine-tuning process.
- Lower Memory Usage: Traditional fine-tuning can be memory-intensive, especially with large models. PEFT addresses this by limiting the number of parameters that need to be stored and updated. This makes it feasible to deploy advanced models on devices with limited memory, such as smartphones or edge devices.
- Faster Fine-tuning and Deployment: Because PEFT focuses on a smaller subset of parameters, the time required to fine-tune a model is significantly reduced. This speed advantage is crucial in industries where rapid deployment of models can provide a competitive edge.
- Maintains Model Performance: Despite reducing the number of parameters being updated, PEFT techniques are designed to retain, and sometimes even enhance, the performance of the model. This balance of efficiency and effectiveness makes PEFT a highly attractive option for many machine learning tasks.
Applications of Parameter-efficient Fine-tuning (PEFT)
PEFT is being utilized across various domains due to its flexibility and efficiency. Some notable applications include:
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): In NLP, PEFT is used to fine-tune language models for specific tasks like sentiment analysis, translation, or summarization. By only adjusting essential parameters, models can be quickly adapted to new languages or domains without extensive retraining.
- Computer Vision: For image recognition and other computer vision tasks, PEFT allows models to be tailored to new datasets with minimal adjustments. This is particularly useful in fields like medical imaging, where models must adapt to new types of scans or imaging techniques.
- Speech Recognition: In speech recognition, PEFT helps in customizing models to understand different accents, dialects, or even languages by fine-tuning a select set of parameters. This leads to more robust and adaptable speech recognition systems.
- Robotics and Autonomous Systems: Parameter-efficient fine-tuning can also be applied in robotics, where models need to quickly adapt to new environments or tasks. By minimizing the computational burden, PEFT enables robots to learn new skills on the fly without requiring extensive retraining.
Challenges and Future Directions
While parameter-efficient fine-tuning offers numerous advantages, it is not without challenges. One of the key issues is identifying which parameters are the most critical to update, as incorrect selection can lead to suboptimal performance. Additionally, as models become increasingly complex, finding the right balance between parameter efficiency and model accuracy will be essential.
Looking ahead, research in PEFT is likely to focus on developing more sophisticated techniques for parameter selection and adaptation. There is also potential for integrating PEFT with other advancements in machine learning, such as transfer learning and meta-learning, to further enhance its capabilities.
Conclusion
Parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) represents a significant step forward in making machine learning models more accessible and adaptable. By reducing the need for extensive parameter updates, PEFT enables faster, cheaper, and more efficient model fine-tuning, opening up new possibilities for deployment across a wide range of applications. As the field continues to evolve, PEFT will likely play a crucial role in the next generation of AI advancements, making sophisticated models more practical for everyday use.
Whether you are working in NLP, computer vision, or any other area of AI, understanding and leveraging PEFT can provide substantial benefits, making it a valuable tool in the modern machine learning toolkit.
Leave a comment