In the rapidly evolving field of machine learning, particularly in natural language processing (NLP), researchers and practitioners are constantly seeking methods to improve model performance while minimizing resource consumption. One such method that has gained significant attention is parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT). This article will provide an overview of PEFT, its benefits, various techniques involved, and considerations for model training.
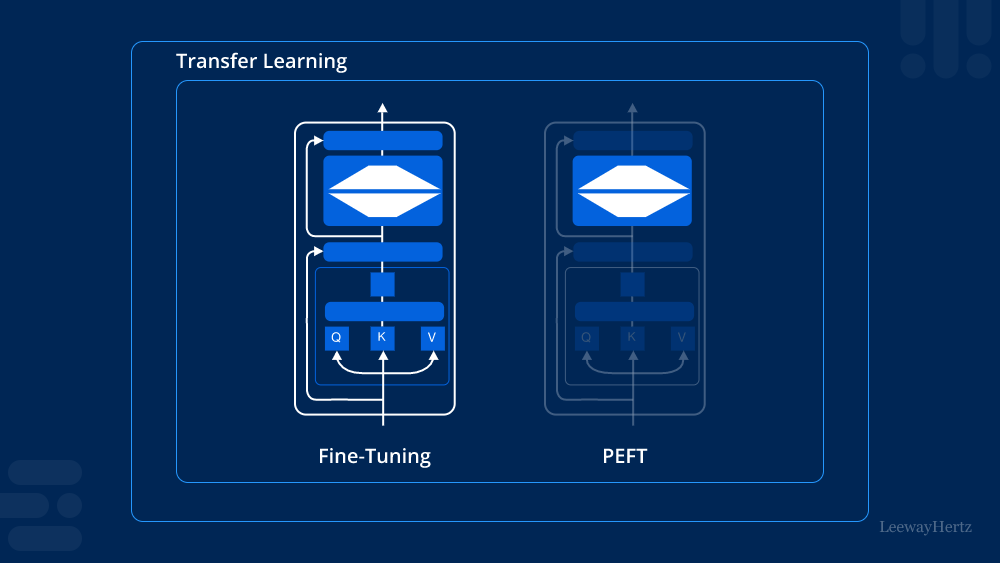
What is Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT)?
Parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) refers to a set of strategies that optimize the fine-tuning process of pre-trained models by adjusting only a small subset of their parameters. Instead of updating all model parameters during training, PEFT focuses on modifying a limited number, significantly reducing the computational resources and time required for training. This approach is especially beneficial in scenarios where computational power is limited or when deploying models in real-time applications.
Benefits of Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT)
1. Reduced Computational Costs
One of the primary advantages of PEFT is the reduction in computational costs. By fine-tuning only a fraction of the parameters, organizations can save on both training time and energy consumption. This makes PEFT particularly appealing for researchers and developers working in environments with limited resources.
2. Faster Training Times
In addition to reducing computational costs, PEFT also leads to faster training times. Since fewer parameters are being adjusted, the training process can be completed more quickly. This is crucial for applications that require rapid model deployment and iteration.
3. Improved Generalization
Parameter-efficient fine-tuning often leads to better generalization of models. By carefully selecting which parameters to fine-tune, it is possible to retain the pre-trained model’s knowledge while adapting it to specific tasks. This balance helps improve performance on downstream applications without overfitting.
4. Accessibility for Smaller Teams
PEFT democratizes access to advanced machine learning models. Smaller teams or organizations with limited resources can still leverage powerful pre-trained models without the need for extensive computational infrastructure. This can drive innovation and broaden the scope of projects that can be undertaken.
Techniques in Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT)
Several techniques fall under the umbrella of parameter-efficient fine-tuning. Each has its unique approach to optimizing model training while preserving efficiency.
1. Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA)
Low-rank adaptation (LoRA) is a technique that decomposes weight updates into low-rank matrices. This allows for fewer parameters to be updated, as the changes can be expressed in a more compact form. LoRA has shown promising results in various NLP tasks and is favored for its efficiency and effectiveness.
2. Adapter Layers
Adapter layers are small, trainable modules inserted between the layers of a pre-trained model. During fine-tuning, only these adapter layers are updated while the rest of the model remains frozen. This technique allows for the model to maintain its general knowledge while adapting to specific tasks efficiently.
3. Prompt Tuning
Prompt tuning involves designing specific prompts or inputs that guide the model’s behavior without needing to alter its parameters significantly. This technique is particularly useful in NLP, where prompts can be crafted to elicit desired responses from a model while keeping the underlying architecture unchanged.
4. BitFit
BitFit is a minimalist approach that fine-tunes only the bias terms in a model. This method is incredibly lightweight, making it an attractive option for applications where only minor adjustments are necessary to achieve satisfactory performance.
Considerations for Model Training with PEFT
While parameter-efficient fine-tuning offers numerous advantages, there are important considerations to keep in mind during model training.
1. Task Compatibility
Not all tasks may benefit equally from PEFT. It is essential to evaluate the compatibility of a chosen PEFT technique with the specific task at hand. Some tasks may require more extensive fine-tuning to achieve optimal performance.
2. Model Size
The size of the pre-trained model can influence the effectiveness of PEFT strategies. Smaller models may have fewer parameters to begin with, which could limit the benefits of parameter-efficient fine-tuning. It is important to select a model that aligns well with the chosen technique.
3. Monitoring Performance
During the fine-tuning process, continuous monitoring of the model’s performance is crucial. Evaluating the model against validation datasets can help ensure that the selected PEFT method is yielding the desired improvements without overfitting.
4. Iterative Approach
An iterative approach to fine-tuning is often beneficial. Experimenting with different techniques and monitoring their impact on performance can lead to optimal results. Flexibility in adjusting methods as needed can enhance the fine-tuning process.
Conclusion
Parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) is a transformative approach in the realm of machine learning, allowing for efficient adaptation of pre-trained models to specific tasks. With its array of techniques, PEFT not only reduces computational costs and training times but also promotes broader accessibility to advanced modeling capabilities. As the demand for efficient model training continues to grow, the relevance and application of PEFT are likely to expand, driving innovation and enhancing the effectiveness of machine learning solutions.
Leave a comment