Generative AI is a rapidly evolving field that leverages advanced algorithms to create content, designs, and solutions across various industries. This technology holds the potential to transform how we approach tasks, enabling creativity and efficiency in ways previously thought impossible. In this article, we will explore the use cases, applications, and solutions offered by generative AI, along with its implementation challenges and opportunities.
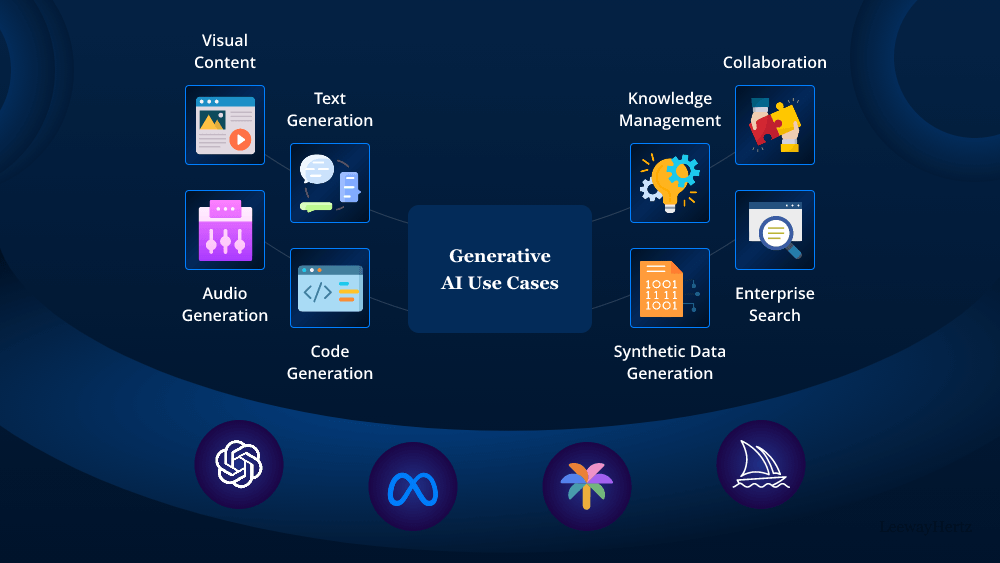
What is Generative AI?
Generative AI refers to a category of artificial intelligence that focuses on generating new content, data, or solutions based on learned patterns. By analyzing vast amounts of data, these models can produce text, images, music, and even code. Unlike traditional AI, which primarily analyzes data, generative AI creates new information, opening doors to innovative applications.
Use Cases of Generative AI
Content Creation
One of the most prominent use cases of generative AI is content creation. This includes generating articles, social media posts, and marketing materials. With the ability to analyze existing content, generative AI can produce high-quality writing that aligns with specific tones, styles, and topics, saving time for writers and marketers.
Design and Art
In the realm of design, generative AI has been instrumental in creating stunning visuals, graphics, and even architectural designs. By using algorithms that learn from existing artworks, designers can generate unique pieces that push the boundaries of creativity. This application is particularly useful for graphic designers looking for inspiration or for companies needing custom designs at scale.
Music Composition
Generative AI is also making waves in the music industry. It can compose original pieces by learning from existing songs and musical patterns. This technology allows musicians to explore new genres, create soundtracks, and even personalize music for specific audiences. With the help of generative AI, the creative process becomes more efficient and diverse.
Software Development
In software development, generative AI can assist in writing code, debugging, and creating software prototypes. By analyzing coding patterns, these models can suggest improvements, generate boilerplate code, and even automate repetitive tasks. This application enhances productivity and reduces the time required to bring software solutions to market.
Applications of Generative AI
Healthcare
Generative AI is making significant strides in the healthcare sector. It can assist in drug discovery by simulating molecular interactions and generating potential compounds for testing. Additionally, generative models can analyze patient data to create personalized treatment plans, thereby improving patient outcomes and optimizing resources.
Gaming
The gaming industry is another area where generative AI shines. It can create realistic environments, characters, and narratives, enhancing the overall gaming experience. By using generative models, game developers can produce vast, dynamic worlds that adapt to players’ choices, leading to more immersive gameplay.
Marketing and Personalization
In marketing, generative AI enables highly personalized campaigns by analyzing consumer data. By generating tailored content, businesses can engage their audiences more effectively, improving conversion rates. This application not only enhances customer experiences but also maximizes marketing ROI.
Solutions for Implementing Generative AI
Data Collection and Preparation
Successful implementation of generative AI begins with data collection and preparation. Organizations need to gather high-quality datasets that reflect the content they wish to generate. This may involve curating existing data, cleaning it, and ensuring it is representative of the desired output.
Model Selection and Training
Choosing the right generative model is crucial. Depending on the application, organizations can select from various models, such as GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks), VAEs (Variational Autoencoders), or transformer-based models. After selection, training the model on the prepared dataset is essential for optimal performance.
Integration and Deployment
Once trained, the generative AI model needs to be integrated into existing systems. This may involve developing APIs or embedding the model into applications. Ensuring scalability and reliability during deployment is crucial for organizations to reap the benefits of generative AI.
Continuous Monitoring and Improvement
After deployment, continuous monitoring is vital to assess the model’s performance. Organizations should track user feedback, engagement metrics, and output quality to identify areas for improvement. Regular updates and retraining of the model may be necessary to maintain relevance and effectiveness.
Conclusion
Generative AI is reshaping various industries through its diverse use cases and applications. From content creation to healthcare and gaming, this technology is driving innovation and efficiency. However, successful implementation requires careful planning, data preparation, and ongoing optimization. As organizations continue to explore the potential of generative AI, its transformative impact will only grow, paving the way for a future rich in creativity and productivity.
Leave a comment